CROHMIQ® Type D FIBC

CROHMIQblue™ was the world’s first FIBC fabric to provide full protection against electrostatic hazards without the need for grounding … it is the original Type D FIBC fabric.
CROHMIQblue™ and CROHMIQwhite™ are the number one static protective packaging materials for leading global companies.
25-50-100 Safety Record™ – For more than 25 years, over 50 million CROHMIQ FIBC have been safely used to package and transport over 100 billion pounds of products for industries most demanding applications, without any electrostatic hazard incidents.
Type B FIBC
because brush discharges from Type B FIBC can cause explosion!
Dangers of Type B
Type B FIBC are only safe for use in non-combustible environments or where the only combustible material is a powder, e.g. flour, sugar, etc.
Type B FIBC cannot be used as a safe alternative to Type D FIBC for operations involving low ignition energy flammable powders (e.g. bisphenol-A) or flammable gases or solvent vapours (e.g. pentane, toluene).
Many pigments, additives and other chemicals used in paint and coatings manufacturing are non-combustible, e.g. titanium dioxide, calcium carbonate, etc., so there are no electrostatic risks when FIBC are filled.
However, if FIBC are emptied into solvent-based processes, there is a very high risk of fire or explosion, because:
• electrostatic charging occurs when FIBC are emptied, and
• solvent vapours are easily ignited by electrostatic discharges from unprotected FIBC, such as Type B FIBC
End-users who may be at risk and should never accept Type B FIBC as an alternative to CROHMIQ Type D FIBC.
Standards & Codes of Practice
All relevant safety standards and codes of practice clearly state that Type B FIBC shall not be used if a flammable gas or solvent vapour is present:
• IEC TS 60079-32-1 & IEC 61340-4-4 (International)
• NFPA 77, NFPA 652 and NFPA 654 (US)
• CLC/TR 50404 (Europe)
• TRGS 727 (Germany)
• JNIOSH TR No. 42 (Japan)
Referring to Table 5 in IEC 61340-4-4: 2018 and Table 16.3.3 in NFPA 77: 2024 (copied below) it is clear that Type B FIBC are not permitted in areas where flammable gases or solvent vapours are present.
IEC 61340-4-4: 2018 Table 5 – Use of different types of FIBC
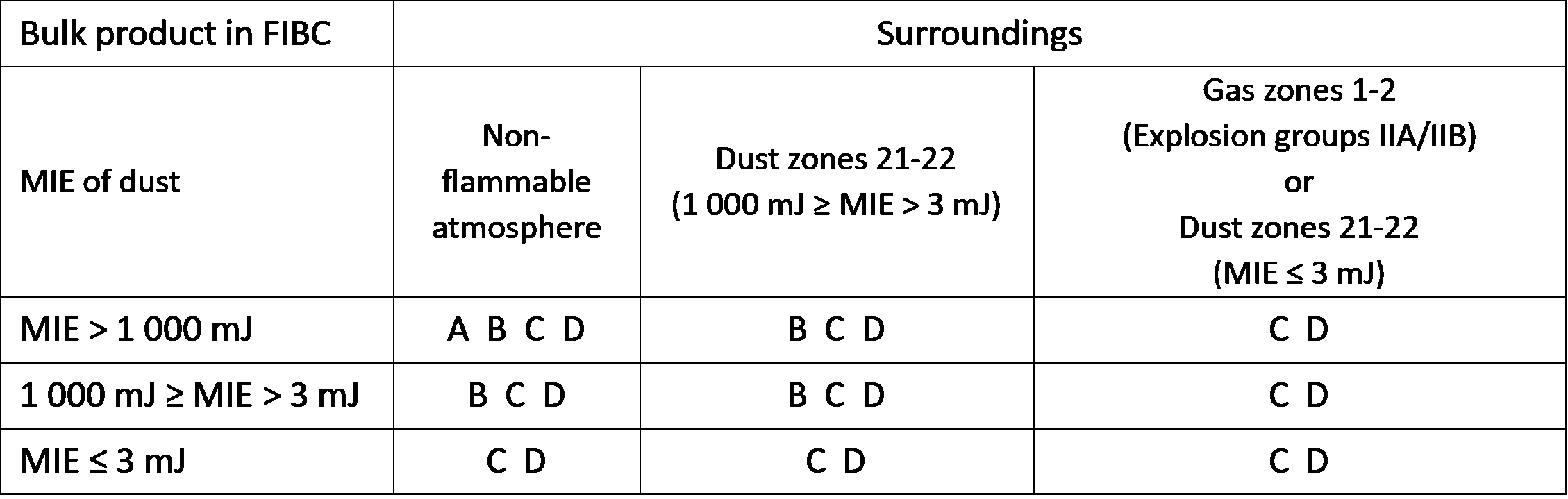
NFPA 77: 2024 Table 16.3.3 – Use of different types of FIBCs
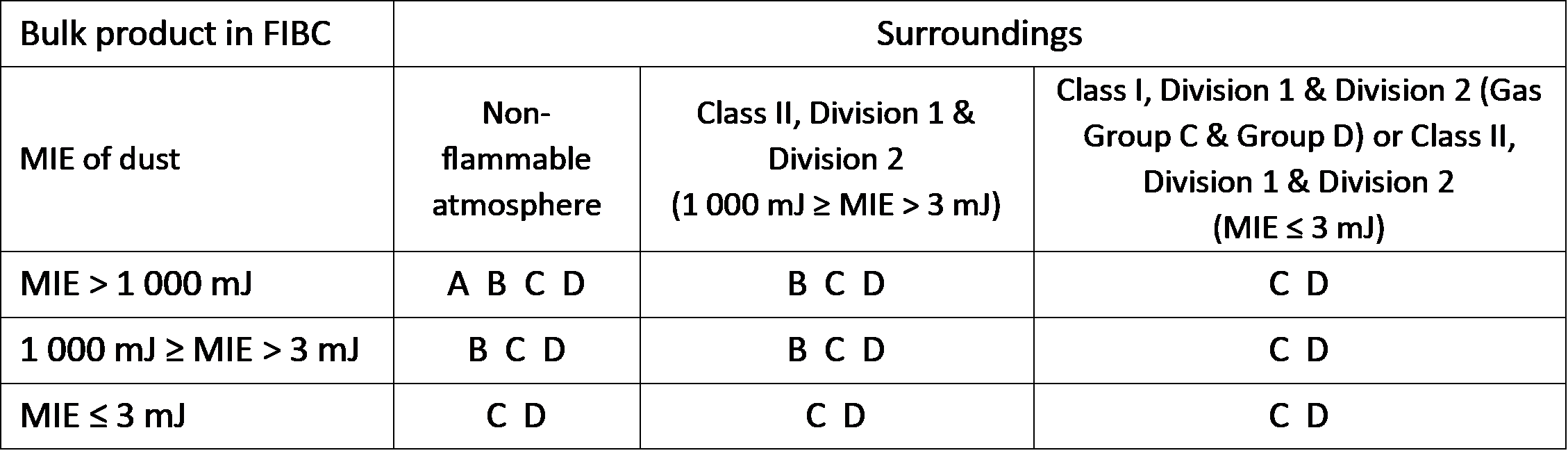
Labelling requirements

The label does not permit the use of Type B FIBC in hazardous gas zones (Zone 1 and Zone 2/Class I, Division 1 and Division 2).
Dangers of switching from Type D FIBC to Type B FIBC
Companies that receive chemicals or EPS in Type D FIBC will have carried out risk assessments to ensure that the packaging is safe for their operations.
Before any change can be made to their processes, including the type of packaging used, risk assessments must be carried out to ensure that safety is not compromised.
Companies supplying chemicals or EPS must take account of the receiving companies’ packaging risk assessments.
Switching from Type D FIBC to Type B FIBC constitutes a significant reduction in safety, and doing so without full risk assessment has the potential to create explosion risks at end-user facilities.
