| Propagating Brush Discharges | 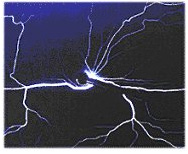 |
Occur on insulating sheet materials with high dielectric strength when both surfaces are highly charged, but to opposite polarity. Avoided in FIBC by ensuring breakdown voltage of sheet materials is low. |
|---|---|---|
| Sparks | 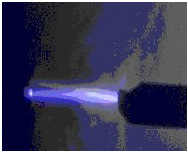 |
Occur between two conductors, e.g. conducting threads in groundable Type C FIBC and metal frame. Avoided by grounding all conductors, including conductive Type C FIBC, support frames, tools, personnel, etc. |
| Cone Discharges | 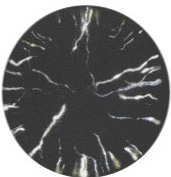 |
May occur when filling all types of FIBC with non-conductive powder. Space charge density increases as powder is compacted. The high field created can result in large discharges running across the cone of powder. Risk can be reduced by filling more slowly. |
| Brush Discharges | 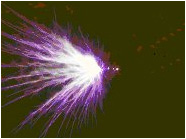 |
Occur between insulating surfaces and conductors. No evidence of igniting dusts, but may ignite sensitive gas and vapour atmospheres. Occur from all types of FIBC but energy reduced in Type C FIBC by limiting the area between conducting threads and in Type D FIBC by reducing surface charge density. |
| Corona | 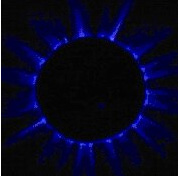 |
Occurs from pointed conductors or those with a small radius of curvature, e.g. fine wires or conducting threads. High field at the surface of sharp conductors causes surrounding air to be ionised. Energy is released slowly and continuously, which does not cause ignition except in the most sensitive gas mixtures (e.g. oxygen rich flammable gases). Corona is used beneficially CROHMIQ Type D FIBC to safely dissipate charge into the surrounding atmosphere. |
Scroll or view in landscape mode to see full table.
