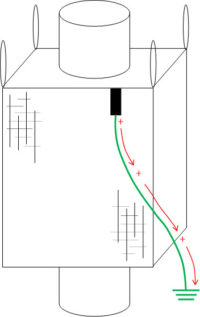
Interconnected Conductive Threads
Dissipates Charge to Ground
RG < 108 ohm
Safe use:
- To transport flammable powders
- When flammable solvents or gases are present around the bag
Do not use:
- When ground connection is not present or has become damaged
Type C FIBC are also known as conductive FIBC or groundable FIBC. Originally they were made from entirely conductive materials. Today, groundable Type C FIBC are more commonly made from non-conductive polypropylene interwoven with conducting yarns, normally in a grid pattern. The conductive yarns must be electrically interconnected and connected to designated ground or earth bonding points. The ground or earth bonding points must in turn be connected to a system ground or earth during all bulk bag filling and emptying operations.
The interconnection of conductive yarns and the connection to ground or earth are critical to the safe use of Type C FIBC. The interconnection of conductive yarns throughout the bulk bag is achieved by correctly sewing together the panels of fabric that make up the groundable bulk bag. Sewing is a manual operation, as is the connection of the groundable bulk bag to a system ground or earth. As with any manual operation, ensuring interconnection and grounding of Type C FIBC is subject to human error. In his case study review published in “Process Safety Progress”, Vol. 12. No. 4. October (1993) , Dr Lawrence G. Britton, in referring to the dangers of ungrounded Type C FIBC, stated “In particular it should be appreciated that the potential for operator grounding error and sudden nemesis can be very high”.
Many companies concerned about the very serious dangers of ungrounded Type C FIBC choose to use the safe option of CROHMIQ Static Protective Type D FIBC that provide full electrostatic protection without the need for grounding.
