Warning: Uninitialized string offset 19 in /home/d0dchcz16k7v/public_html/wp-content/plugins/fusion-builder/shortcodes/fusion-table.php on line 119
TEXENE es el líder mundial líder y reconocido en tejido protector estático sin conexión a tierra para FIBC Tipo D (Antiestático). Como parte de su compromiso en marcha con la seguridad y el desarrollo de productos, la compañía mantiene una instalación de pruebas de rendimiento de seguridad FIBC a gran escala en Miami Lakes, Florida, EE. UU. Esta instalación de 12,000 pies3 ambientalmente controlada incorpora dos laboratorios, cada uno diseñado y equipado para cumplir con los requisitos del estándar de prueba internacional, IEC 61340-4-4 Ed. 3.0. El laboratorio está dirigido por el Dr. Paul Holdstock, quien posee un doctorado en electrostática.
Dentro de la instalación de prueba, FIBC a gran escala se llena y vacía en condiciones de carga electrostática que simulan entornos industriales. Los parámetros de prueba incluyen FIBC conectado a tierra (para bolsas a granel de tipo C) o sin conexión a tierra (para bolsas a granel de tipo D), temperatura, humedad relativa y velocidad de carga electrostática. Las mediciones de rendimiento de la FIBC incluyen transferencia de carga, potencial de superficie y pruebas de inendividad utilizando una sonda de gas con mezclas específicas para una gama de energías de ignición mínimas. Además de las pruebas de bolsas a granel, el laboratorio de electrostática se utiliza para medir las propiedades electrostáticas, como la resistividad superficial, el voltaje de descomposición de los tejidos, la resistividad lineal y la resistencia a los puntos de conexión a tierra.
Para garantizar la seguridad continua de la FIBC Tipo D sin conexión a tierra y en tierra fabricada a partir de tejido CROHMIQ, Texene realiza regularmente pruebas en su laboratorio de pruebas de rendimiento de seguridad bajo el Programa de Certificación de Seguridad Continua™.
La Certificación de Seguridad Continua (CSC) es un programa único proporcionado por Texene a sus clientes y usuarios finales. El Programa CSC implica la calificación de seguridad inicial de las bolsas a granel de protección estática CROHMIQ para garantizar que cada diseño cumpla con los requisitos esenciales de seguridad de IEC 61340-4-4 para FIBC tipo D. Después de la calificación inicial de seguridad, se vuelven a probar muestras aleatorias de producción de bolsas a granel CROHMIQ para garantizar que siguen proporcionando la seguridad requerida por los usuarios finales.
La prueba más importante que demuestra la seguridad de FIBC para su uso en atmósferas inflamables o explosivas es la inendividad, o prueba de ignición. El principio es llenar la bolsa a granel bajo prueba con pellets cargados y determinar si hay descargas electrostáticas de la superficie de la bolsa a granel con energía suficiente para encender una sonda de gas que se aproxima. Los parámetros de prueba se seleccionan para proporcionar el desafío más grave a FIBC antiestático para garantizar que puedan funcionar de forma segura en las peores condiciones. Los parámetros críticos de la prueba y la importancia de cada uno se describen a continuación.
Parámetros de prueba y su importancia
| Temperture & Humidity | The electrostatic properties of polymeric materials depend to a greater or lesser extent on the amount of moisture they are able to absorb from the atmosphere. There is too little moisture available at low relative humidity and so static charge tends to accumulate more readily and dissipate more slowly.
Some materials absorb a lot of moisture and at high relative humidity their resistance can be so low that spark discharges may occur if the materials are isolated from ground. To ensure that CROHMIQ Type D bulk bags are able to maintain safe charge dissipation without becoming too conductive, it is necessary to test at both low and high relative humidity. |
|---|---|
| Charging current | The rate at which charge flows into and out of a bulk bag depends on the speed of filling and emptying and the chargeability of the product. Charging current is the charge flow rate expressed as ampere (A), or more conveniently micro-ampere (µA).
End-user data has shown that sustained charging currents of about 3 µA are possible, with transients sometimes even higher. It is necessary to test using charging currents that replicate those found in industry. |
| Minimum Ignition Energy (MIE) | MIE is the smallest quantity of energy in an electrostatic discharge required to cause the ignition of a gas, vapor or powder. MIEs are normally expressed in milli-joule (mJ). The severest incendivity test is to use a gas mixture with the lowest practically relevant MIE.
Methanol vapor has the lowest MIE of any gas or solvent that is likely to be present when bulk bags are emptied. The MIE for methanol is 0.14 mJ. Click here for MIE of other common substances. |
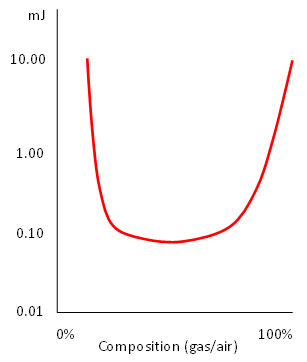
| Gas Composition | The gas selected for incendivity testing is mixed with air to achieve the required MIE. The ratio of gas to air must be controlled to tight tolerances in order to maintain the specified MIE throughout the test. Furthermore, the composition of the air used must also be controlled.
MIE normally changes with gas composition in a way similar to that shown below:
Small changes in gas composition can produce a dramatic increase in MIE, making it easier to pass the test. Precise control of the gas composition is essential if the severity of the test is to be maintained. |
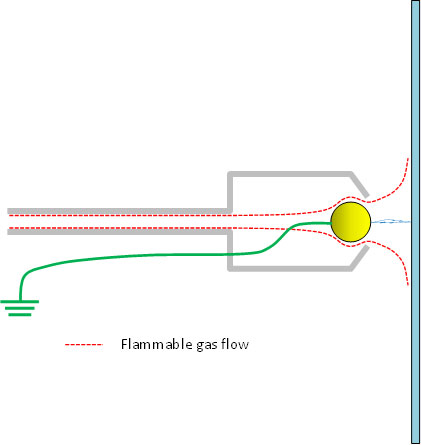
| Gas Flow Rate | The gas probe used for incendivity testing is a grounded metal electrode surrounded by a shroud that directs a flow of gas in front of the electrode, as shown below:
As gas exits the probe it is diluted by the surrounding air. It is necessary to minimize dilution because it changes the MIE of the gas. If the gas flow rate is high enough, dilution will not be significant. |
| Number of Repeat Tests | Ignition of a gas by electrostatic discharges is a probabilistic phenomenon. For example, a 1 mJ spark might ignite a 0.1 mJ MIE gas every time, but a 0.1 mJ spark may only ignite the same gas 1 time out of 100.
Confidence of a pass in incendivity testing (i.e. no ignitions) can only be achieved by performing a statistically significant number of gas probe approaches. Furthermore, approaches should be made at different locations on all sides of the bulk bag under test, during filling and emptying. |
Parámetros utilizados para probar CROHMIQ® FIBC
| Temperatura y humedad | (23 a 2) oC / (20 x 5) % de humedad relativa, y
(23 A 2) OC / (60 á 10) %RH |
|---|---|
| Corriente de carga | (3,0 x 0,2) o una polaridad negativa |
| Mie | (0,14 x 0,01) mJ |
| Gas inflamable | Etileno |
| Aire | (21,0 x 0,5% Oxígeno, equilibrio de nitrógeno |
| Composición de gas | (5,4 x 0,1) % Etileno |
| Caudal de gas | (0,21 a 0,04) litros/s |
| Monitoreo de la composición del gas | Analizador de gas de etileno IR que proporciona un monitoreo constante y en tiempo real |
| Comprobaciones de calibración | Antes de cada serie de prueba:
|
| Número de pruebas repetidas | Al menos 50 en cada lado, superior e inferior > (200 por FIBC) |
Resultados de las pruebas
Voltaje de ruptura
| Tela | Valores reportados | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| AZUL CROHMIQ™ | CROHMIQ blanco™ | ||
| 6.5 oz de tela CROHMIQ | 3,1 a 0,3 kV | 3,6 x 0,2 kV | |
| 3 oz de tela CROHMIQ | 2,9 x 0,4 kV | 4,0 a 0,4 kV | |
El tejido CROHMIQ cumple con los requisitos de la Cláusula 7.2 de la Norma Internacional IEC 61340 4-4 Ed. 3.0 (2018) porque la tensión de avería es inferior a 6 kV.
Pruebas de ignición
| Parámetro | Valores reportados | |
|---|---|---|
| Atmósfera para acondicionamiento y pruebas | 23 oC y 20 % DE humedad relativa 23 oC y 60 % DE humedad relativa |
|
| Mezcla de gas inflamable | 5,4% de etileno, aire de equilibrio (21% O2) a 0,21 litros/s | |
| Energía mínima de encendido (MIE) | 0,14 mJ | |
| Tasa de llenado | 1 kg/s | |
| Corriente de carga | 3 A (polaridad negativa) | |
| AZUL CROHMIQ™ | CROHMIQ blanco™ | |
| Número total de intentos de ignición | 432 | 432 |
| Número de igniciones | Cero | Cero |
CROHMIQ FIBC cumple con los requisitos de la Cláusula 7.3.2 de la Norma Internacional IEC 61340-4-4 Ed. 3.0 (2018) porque no se produjeron igniciones.
CROHMIQ FIBC también cumple con los requisitos para fiBC de tipo D según se especifica en: IEC/TS 60079-32-1: 2013, CLC/TR 50404: 2003, NFPA 77: 2019, NFPA 652:2019, NFPA 654:2017 y JNIOSH TR No. 42:2007.
Seguridad de los procesos de T-V S-D Schweiz AG (Informes de prueba 923533-17-0250-01 & -02)